What is Data Center Infrastructure?
Release time: 2025-06-05
Data center infrastructure, with its four core systems—security, power, cooling, and connectivity—ensures continuous and reliable data services. Its construction costs can be 5-10 times higher than office buildings of comparable scale.
Power System
Power interruptions in data centers are measured in seconds, requiring dual-active redundancy standards:
- Power Chain: A complete path from substation to servers includes transformers, switchgear, UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), PDU (Power Distribution Unit), and RPP (Remote Power Panel). For example, UPS battery modules sustain server operations for over 30 minutes during grid outages, bridging the gap until backup generators activate.
- Contingency Plans: On-site diesel generators (N+1 redundancy) with ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) take over within 10 milliseconds. A large-scale data center may deploy 11×1.5MW generators (supporting 10 at full load), ensuring uninterrupted power even during single-unit failures.
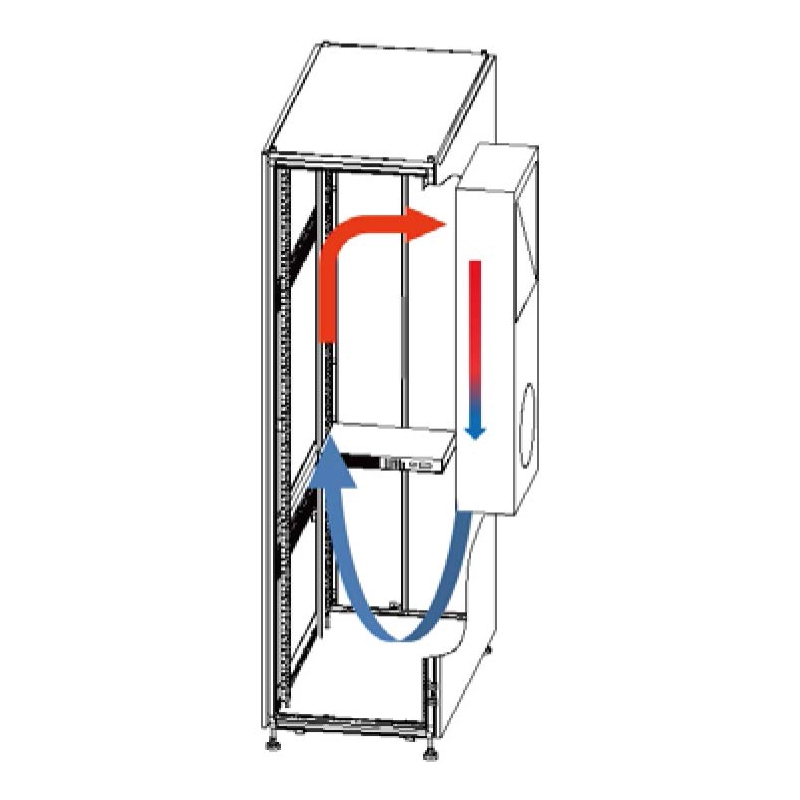
Cooling System
Server racks consume 5-25kW each, making cooling a critical density constraint. Key solutions include:
Traditional Air Cooling:
- Raised-floor airflow: Cold air is delivered through 30cm+ plenums via perforated tiles, while hot air is collected overhead and recirculated via chilled water systems. Ideal for 5-10kW/rack densities.
Innovative Technologies:
- Liquid Immersion Cooling: Servers submerged in 3M Fluorinert leverage evaporative heat transfer, offering 300% higher efficiency than air cooling, supporting 50kW+/rack, and extending hardware lifespan by 20%.
- Free Cooling: In cold climates (e.g., Google’s Finland facility), outdoor air is filtered through air-to-air heat exchangers, cutting mechanical cooling energy by 40-60%.
Data: Hybrid cooling achieves PUE <1.1, reducing energy use by 40% versus traditional air cooling.
Redundancy Design
Redundancy follows “N+x” architecture:
- N+1: Base capacity (N) + 1 backup unit. Example: 10 cooling units +1 spare. Maintains operations during single failures but vulnerable to secondary faults.
- 2N: Fully independent dual systems (e.g., 2×10 units). One system can fully replace the other, critical for healthcare/finance (e.g., <5 minutes annual downtime).
Industry Adoption:
- 90%+ internet data centers use N+1.
- Financial-grade facilities mandate 2N.
The Future of Infrastructure
Data center competitiveness hinges not just on server count but on reliability and innovation. From “millisecond power failovers” to “globally distributed networks”, every layer embodies “availability-first” principles. With AI and edge computing driving demand, high-density, low-PUE, and intelligent infrastructure will define the next generation, steering the digital economy toward greater efficiency and sustainability.